4. Attack Vectors on Blockchains#
“Blockchain technology can solve all our future problems while ensuring security and privacy”
Well, no
Blockchains are not immune to attacks (like any IT system)
Various attack vectors exist [Saad et al., 2020]
Understanding these vectors is crucial for developers and users
Blockchain “hype” led to a false sense of security
According to SlowMist, there were a total of 464 security incidents in 2023, with losses amounting to $2.486 billion [SlowMist, 2024]
over 1.7 Billion USD stolen alone in crypto thefts alone
4.1. Overview of common attacks#
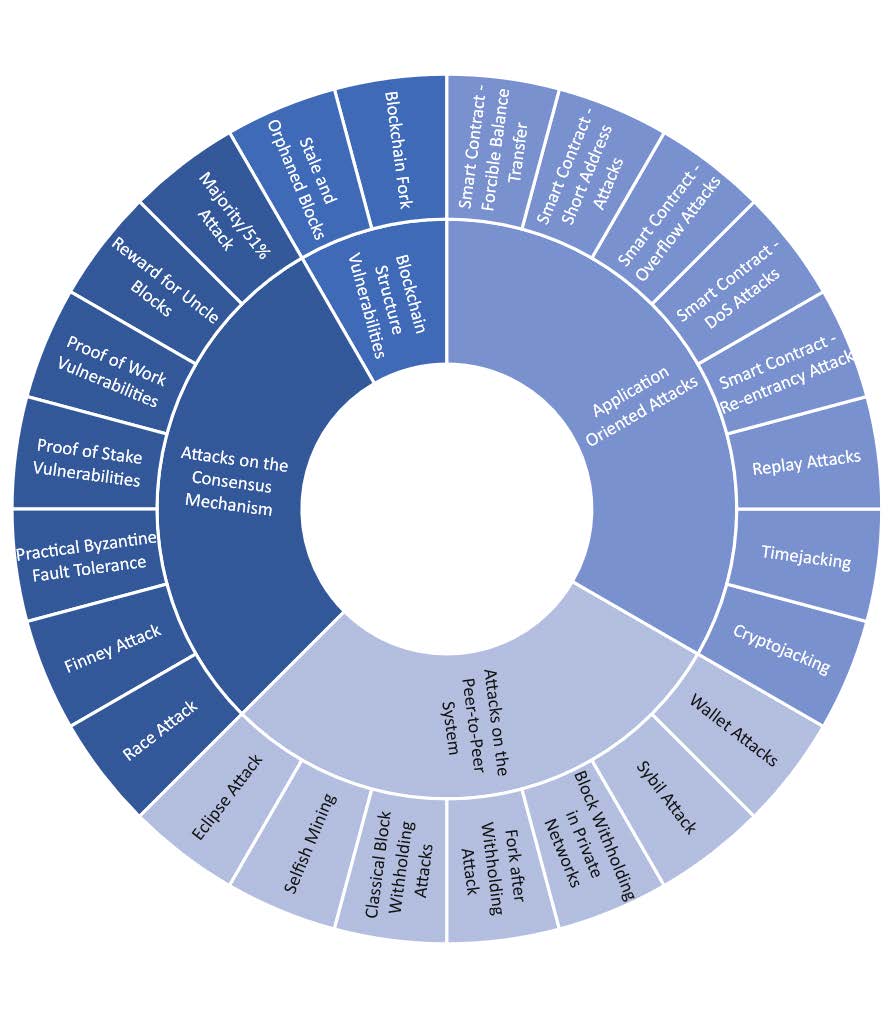
4.2. Types of Attacks#
König et al. divided attacks into four categories [König et al., 2020]
Blockchain Structure Vulnerabilities
Attacks on the Consensus Mechanism
Application Oriented Attacks
Network Layer Attacks
4.2.1. Blockchain Structure Vulnerabilities#
one of the most fundamental risks of blockchain technology
Primarily target integrity, security and availability of the blockchain foundation
Attacks exploit flaws in the fundamental design and implementation of the blockchain
protocols, data structures, transaction processing and recording
byproduct of the technology
Examples:
Blockchain Forks (Soft and Hard Forks, sometimes intentional (DAO Hack revert), sometimes accidental)
Stale and Orphaned Blocks
4.2.2. Attacks on the Consensus Mechanism#
Attacks exploit flaws in the consensus mechanism of the blockchain
target the agreement among participants on the validity of transactions
Examples:
51% Attack
Selfish Mining
Nothing at Stake Attack
Finney Attack
4.2.3. Application Oriented Attacks#
Attacks exploit vulnerabilities in the applications built on top of the blockchain
smart contracts, decentralized applications, wallets, etc.
they exploit the application’s logic and not the blockchain itself
outcome heavily depends on the application’s design and implementation
Examples:
Timejacking
Replay Attacks
Attacks on Smart Contracts and DApps (Overflow attacks, (D)Dos attacks, etc.)
4.2.4. Network Layer Attacks#
Attacks exploit vulnerabilities in the peer-to-peer network (the backbone of blockchain technology)
network attacks nothing new, however distributed nature of blockchain networks further complicates them
attacks aim to disrupt communication, isolate node or manipulate transmissions
Examples:
Eclipse Attack
Block Withholding Attack
Sybil Attack
